How to Reduce the House Edge in Blackjack
In the rules of blackjack, even when playing with the optimal strategy, the dealer still holds a 0.6% advantage. So, how to reduce the house edge in blackjack?

Game Introduction
In the rules of blackjack, even when playing with the optimal Blackjack Strategy, the dealer still holds a 0.6% advantage. This means that on average, a player will lose $6 for every $1000 wagered. So, how to reduce the house edge in blackjack?
If players collaborate and communicate effectively, they can employ a method where the first player makes minimal bets to gather information. Then, by card counting, they can calculate the remaining expected value to determine whether to hit or increase their bets. This collaborative card counting method was successfully used by students from MIT, Caltech, and Harvard in 1979. However, they were later blacklisted by casinos. This story was adapted into the movie "Bringing Down the House" in 2003 on how to reduce the house edge in blackjack.
Quantum Entanglement Solution in Blackjack
Even when players cannot directly transmit information, students from MIT and Caltech proposed a method that utilizes the properties of quantum entanglement. By leveraging the entanglement of quantum bits (qubits), even with only one qubit of information (to decide whether to "hit" or "stand"), it is possible to overcome the dealer's advantage.
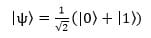
Quantum bits differ from classical bits in that they can exist in a superposition of states, such as 0 and 1, and multiple quantum bits can be entangled, meaning that the measurement of one qubit affects the state of another. An example of a quantum bit in a superposition state is as follows:
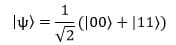
In this example, we observe that the quantum bit is in a superposition state of 0 and 1 until we measure it, at which point the quantum bit collapses probabilistically into either 0 or 1. Another example is a superposition state of two qubits:
Suppose we have a quantum state of two qubits, represented as |ψ〉. When we measure the first qubit, if the result is 0, the second qubit automatically becomes 0 at that moment. If the result is 1, the second qubit automatically becomes 1.
How to Reduce the House Edge in Blackjack
In the rules of Blackjack Strategy, each player and the dealer are dealt an initial open card, followed by a second card dealt face down, visible only to the player. Based on these two cards, players decide whether to hit or stand. If the total point value exceeds 21 after hitting, the player loses the bet. After all players have completed their moves, the dealer decides whether to continue hitting. If the dealer exceeds 21, the players win their bets from the dealer. If the dealer does not exceed 21, the player with the higher point value wins, and in case of a tie, the bets are returned, while the player with the lower point value loses their bet.
In summary, the situations in blackjack can be categorized into the following three possibilities:
- Player loses, dealer wins: The player's total point value exceeds 21 after hitting, or the player's point value is lower than the dealer's when compared at the end.
- Player and dealer push: The player's point value is the same as the dealer's when compared at the end.
- Player wins, dealer loses: The player's point value is higher than the dealer's when compared at the end, or the player's total point value after hitting is not greater than 21, but the dealer's total point value after hitting exceeds 21.
In this article, we consider a scenario with only two players, where the first player, Alice, bets zero. Alice's task is to transmit information to the second player, Bob, through her choice of "hit" or "stand." We map the actions of the two players to the measurement results of the quantum bits, represented as |0〉 or |1〉. By analyzing the cards held by each player and the facedown card, we design a method that utilizes the properties of quantum bits to beat the dealer. The quantum circuit designed for this purpose is as follows:
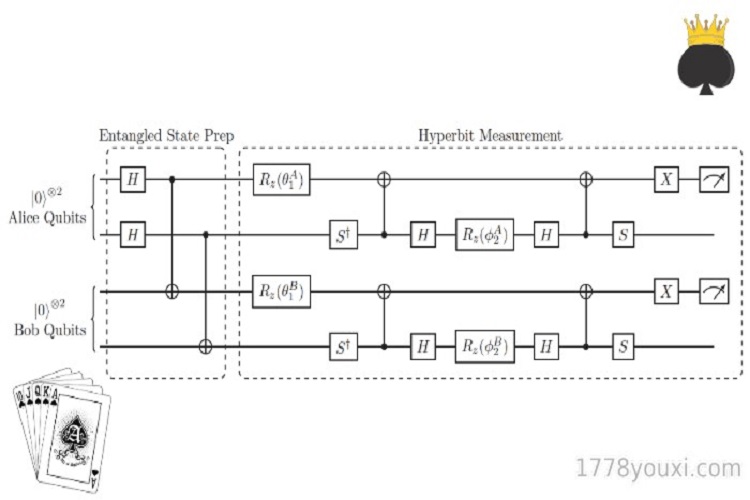
The first box aims to generate entanglement between Alice and Bob, while the second box can be seen as the operations performed by Alice and Bob on the quantum bits based on their cards, with the final measurement determining whether to hit or stand. After studying thousands of rounds of games, it has been shown that Alice and Bob have a slight advantage over the dealer. Although this Blackjack Strategy currently only applies to two players and can only beat the dealer's advantage when there are fewer than eight cards remaining in the deck, it reveals the potential of quantum information in the future.
How to Reduce the House Edge in Blackjack Summary
In the end, can this method be extended when the deck is larger? Should casinos worry about someone exploiting this method to crack the dealer's advantage? On this matter, an expert stated, 'To implement this method in a casino, you might need to carry a quantum computer to calculate changes in the game, but currently, it's practically impossible. Therefore, I believe casinos don't need to worry about these issues at the moment.' However, personally, I think in the possible future 10-15 years, with the emergence of quantum computers capable of implementing Shor's algorithm, applying the properties of quantum computers in casinos could become a possibility. Casinos might adopt a similar approach to other major online companies, designing a new encryption method to ensure that the dealer's advantage cannot be cracked by quantum computers.
 |
 |
Blackjack Strategy













